Boats with these hulls move through the water by pushing the water aside and are designed to cut through the water with very little propulsion. Planing This type of hull doesnt push water aside it balances on top of it.
Understanding The Different Types Of Boat Hulls
Boats with displacement hulls move through the water by pushing the water aside and are designed to cut through the water with very little propulsion.

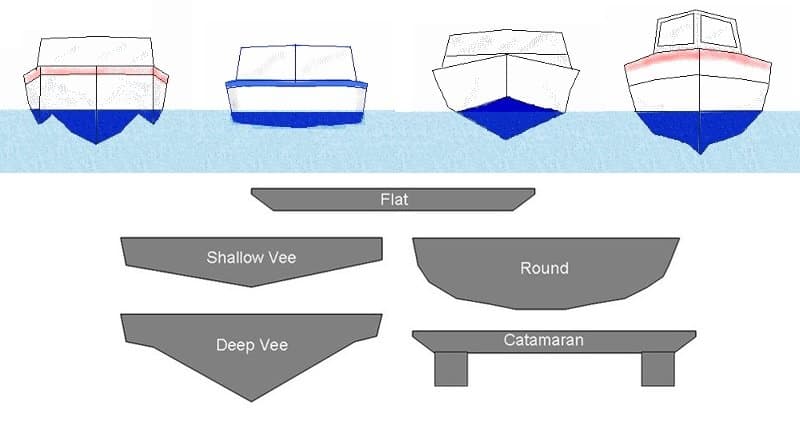
. An iconic Krogen design with a ballasted displacement hull and tremendous storage a proven cruising or liveaboard yacht. Planing hulls come in a variety of shapes each of which has it benefits and disadvantages. Round Bottom Hull 3.
Displacement Hulls There are two basic types of boat hulls displacement and planing. Flat Bottom Hull 2. What is a semi displacement hull.
There are two essential types of powerboat hulls. A displacement hull is an efficient non planing hull that moves through the water at 134 times the square root of the waterline length LWL. With a displacement hull there is no significant advantage in using an engine that will drive the vessel faster than nominal hull speed at 70 or 80 percent of rated RPM.
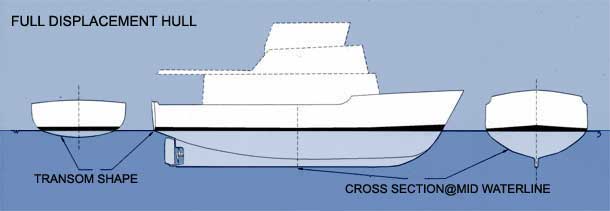
Describing a full displacement hull is very similar. Nothing could be further from the truth. Until hull 65 1985 they were built with glass-over-plywood decks.
The square root of the waterline length LWL multiplied by 134 tells you precisely how fast a displacement hull can go in knots 79 knots for a 35-foot LWL for instance. For example say you have a displacement hull with a waterline length of 25 feet then the hull speed is 5 x 13 7 knots. This type of hull is designed to push through the water moving or displacing the water in a proportion equal to the weight of the boat.
The planing hull is extremely fast and agile. Displacement Hulls That weight is the boats displacement. Maximum hull speed in knots is equal to about 13 X the square root of the waterline length of the hull in feet.
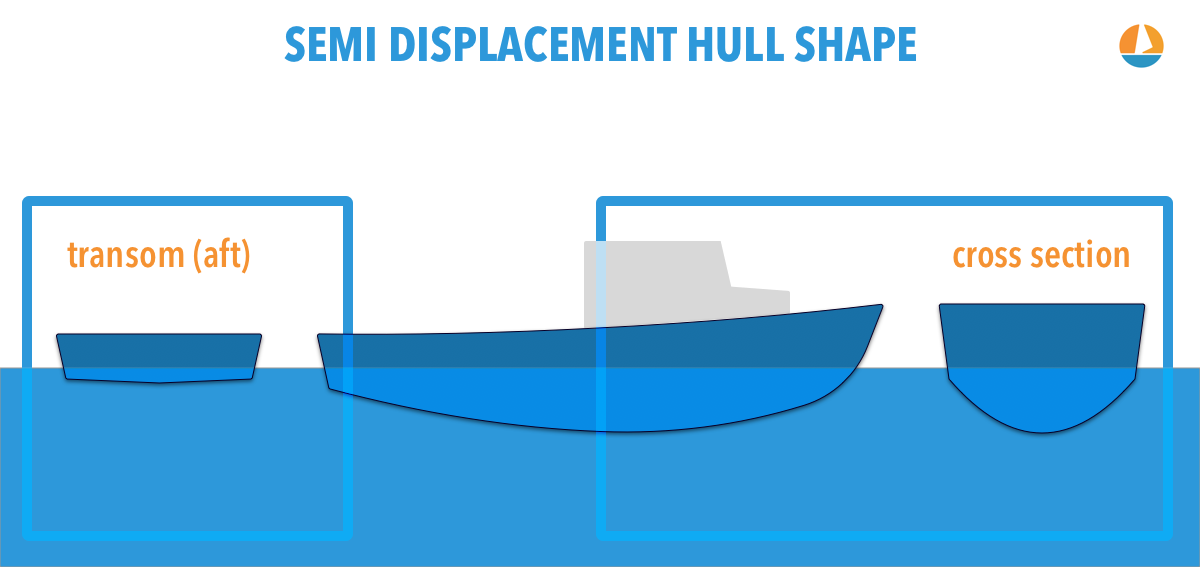
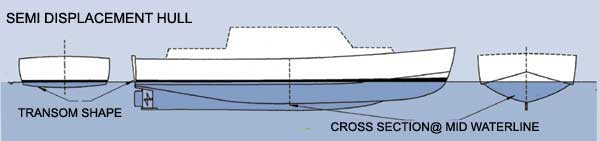
A semi displacement hull creates a big whole in the water which generate large bow and stern waves. What hull is a displacement hull. The amount of water it displaces is equal to its weight.
A round-bottomed hull shape acts as a displacement hull. Deep V Hull 5. With the same amount of horsepower applied hulls with a lower DL ratio will cruise at a faster speed than hulls with a higher DL ratio.
Generally displacement hulls are slow as they are not designed to naturally plan the speed at which they move through the water is limited by its waterline length. The symbol is delta and the units are pounds Kgs or Ton nes. The hull sits deeper into the water and the boat is supported by buoyancy as opposed to its thrust.
Cathedral Hull Size Limits on Planing Hull The Importance of Volume Distribution When Controlling a Boat with a Planing Hull Takeaway Planing Hull vs Displacement Hull Planing Hull. Most large cruisers and most sailboats have displacement hulls allowing them to travel more smoothly through the water. Boats with displacement hulls move through the water by pushing the water aside and are designed to cut through the water with very little propulsion.
Boats with displacement hulls are limited to slower speeds. If you lower a boat into the water some of the water moves out of the way to adjust for the boat. Boats with displacement hulls move through the water by pushing the water aside and are designed to cut through the water with very little propulsion.
And Displacement hulls tend to travel significantly slower than planing hulls due to drag aka friction with the surrounding water. These hulls are typically found on boats that need to carry a heavy load such as a large fishing boat and big yachts. Semi displacement hulls are normally a cross between a planning and displacement hull they will generate an amount of lift but the vessels weight will be supported by buoyancy.
Its units are cubic feet or metres but is rarely seen in any publicity information about boats. Longitudinal symmetry and displacement-to-length ratio DL. We can differentiate between full displacement hulls based upon two form fundamentals.
It lies partially submerged and displaces water when moving hence its name. There are two basic types of boat hulls displacement and planing. Thereafter they were built with a cored deck and superstructure.
Displacement volume V is as the name suggests the volume of water displaced by a floating vessel of a given displacement weight. A displacement hull and a planing hull. The hull is solid fiberglass below the waterline and cored above.
Displacement Hull Planing Hulls and its Various Types 1. The weight of the ship itself. Displacement Hulls The first variety of hulls that we shall examine are displacement hulls.
A displacement hull is a boat hull design that uses buoyancy to support its weight. What is displacement hull. Displacement hulls work be dividing and cutting their way through the water.
Boats with displacement hulls are limited to slower speeds. Thats why this design is widely used on cruisers and sailboats. Boats with these hulls are designed to rise up and glide on top of the water when enough power is supplied.
All three of these hull types come with their own unique advantages and disadvantages. They behave like displacement hulls at low speed but pop up onto a plane usually around 15-16 MPH depending on the design and load. This type of haul is very efficient despite being deeper withing the water than a planing hull.
Such low-speed capability greatly reduces a skippers options when trying to avoid bad weather at a. Its seaworthy and can be. Advantages of Displacement Hulls.
The semi-displacement hull is a bit of both. A round-bottomed hull shape acts as a displacement hull. The displacement hull is efficient and very dependable in rough waters.
Unfortunately many people tend to think that all full displacement vessels are the same. A rough estimate of horsepower for displacement type hulls is fairly simple. That weight is the boats displacement.
Its very stable in rough waters. If you lower a boat into the water some of the water moves out of the way to adjust for the boat. These vessels cut through the water very smoothly even in rough water but move relatively slowly.
These boats may operate like displacement hulls when at rest or at slow speeds but climb. A semi-displacement hull displaces water at low speeds but is able to semi-plane at cruising speeds. A boat with a displacement hull may ordinarily be distinguished by a deep V shape to its bottom or hull.
Most powerboats and personal watercraft have planing hulls that ride on the water at higher speeds. Although this category of hull has become less common many modern ships like tugboats and cruise ships still rely on displacement hulls. In basic terms it displaces the same amount of water when stationary or moving it is supported by buoyancy and they are typically big round and bulbous.

A Input Semi Displacement Yacht Hull B Modified Yacht Hull Download Scientific Diagram

A Input Semi Displacement Yacht Hull B Modified Yacht Hull Download Scientific Diagram
Srd Is A Better Hull Shape Fast Fuel Efficient Stable
Semi Displacement Hulls Explained Illustrated Guide Improve Sailing
Srd Is A Better Hull Shape Fast Fuel Efficient Stable

0 comments
Post a Comment